Sentence Structure
A) Introduction
Use the best sentence you can to communicate your ideas in the exam.
What is a clause in a sentence?
A clause is a group of words with a (s) subject and a (v) verb.
For example:
(s) Computers (v) are important.
= 1 sentence with 1 clause.
We can have two clauses i.e. two groups of words with a subject and a verb:
Computers are important, but they are dangerous to
Computers are important, but they are dangerous too.
= 1 sentence with 2 clauses.
Three sentence clauses
Computers are important, but they can be dangerous too, so we must be careful.
= 1 sentence with 3 clauses.
Now let's add a fourth!
You’ll have noticed that a sentence is not tha
You’ll have noticed that a sentence is not the same thing as a clause.
A sentence is the group of words that comes between two full-stops and it must be a complete thought that makes sense.
e same thing as a clause.
A sentence is a group of words that comes between two full-stops and it must be a complete thought that makes sense.
However do not give any explanation in your task 1 writing.
1. Simple Sentences
A simple sentence is one clause with a subject and verb
However, it can have more than one subject and more than one verb:
2 subjects:
2 Verbs:
2 subject and 2 verbs:
Learn more about to write correct sentences in our Complete IELTS Writing Task 2 Course
B) Compound Sentences
In this sentence structure, the clauses are joined with the following coordinating conjunctions:
- F = for
- A = and
- N = nor
- B = but
- O = or
- Y = yet
- S = so
Here are some examples of compound sentence structure:
- The word ‘fanboys’ is an easy way to remember the different conjunctions that make up compound sentences. Obvioa
- Computers are important, but they can be dangerous too.
- Formula = SV but SV
- Computers are important, but they can be dangerous too, so we must be careful.
- Formula = SV but SV so SV.
- usly the most common are ‘and’, ‘but’, ‘or’ and ‘so’.
This is wrong:
Computers are used widely in most countries now, and they are a sign of progress, and we must ensure everyone has access to them.
For example:
Two possible corrected versions:
- Computers are used widely in most countries now, and they are a sign of progress. We must ensure everyone has access to them.
- Formula = SV and SV. SV.
- Computers are used widely in most countries now, and they are a sign of progress, so we must ensure everyone has access to them.
- Formula = SV and SV so SV.
Using semicolons
For example:
Learn more about to write correct sentences in our Complete IELTS Writing Task 2 Course
Thinking of ideas for your essay
A simple sentence is one clause with a subject and verb
Many students also worry that their ideas are not interesting enough or they are too boring. The examiner is not looking for you to entertain them. They are looking for you to demonstrate an ability to write an essay in English supported by evidence and relevant examples. There are no extra points for interesting ideas. What the ideas must be is relevant to the question being asked.
Brainstorming
This can sometimes work effectively but often there is no framework for the ideas and it can take a long time.
Step 1
Write some key words
Step 2
Practice with lots of topics
Step 3
Write down as many ideas is you can
Do a course designed by a former IELTS Examiner with hundreds of 5* reviews.
Find out what really improves your score in the exam.
Common Topic Familiarisation
Knowing the common topics of IELTS can be highly useful for the IELTS Writing Task 2 as it allows you to familiarize yourself with recurring themes, enabling you to prepare relevant ideas, arguments, and examples in advance, thereby enhancing your ability to effectively respond to various prompts and achieve a higher score in the exam.
Step 1
Familiarize Yourself with Past Topics
Step 2
Conduct Targeted Research
Step 3
Practice and Remember
Practice brainstorming and outlining essays on various IELTS topics for Writing Task 2. With your acquired knowledge and research, engage in regular practice sessions where you simulate exam conditions and time yourself. Practice generating ideas, organizing arguments, and outlining essays within the allocated time limit for Writing Task 2. This step hones your ability to think critically, quickly generate relevant ideas, and structure your essay effectively. By practicing with different topics, you develop the flexibility to adapt your knowledge and arguments to any given prompt, enhancing your confidence and readiness for the actual exam.
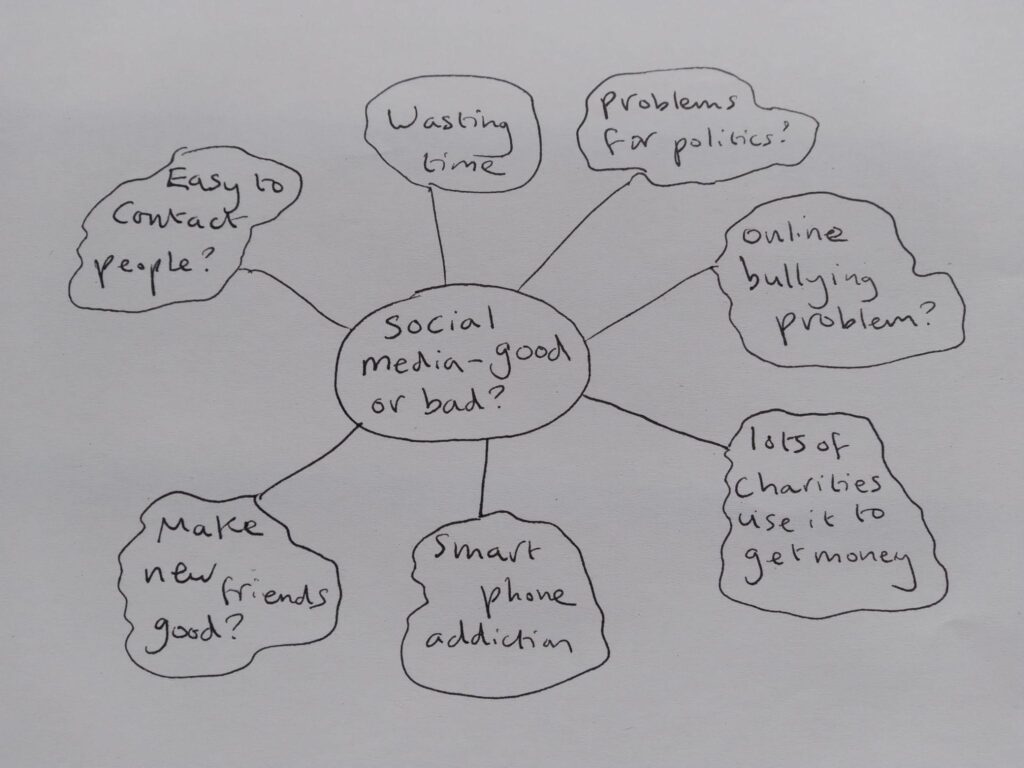
Mind Mapping
Look at the steps below.
Step 1
Write the main topic and subtopics on a piece of paper
Step 2
Expand your map
Once you have a basic structure of branches and sub-branches, start making connections between them. Use lines or arrows to link related ideas together. These connections represent the relationships or associations between different concepts. Expand on each branch by adding more detailed information, keywords, or short phrases. Include images, symbols, or colors to enhance visual appeal and aid in memory retention.

Using semicolons
For example:
Learn more about to write correct sentences in our Complete IELTS Writing Task 2 Course
5 Questions Method
This method uses who/what/why/where/how question words to generate ideas for the writing Task. This works best for people who think very logically and know a little about the topic already.
Look at the steps below.
Step 1
Write the main topic and subtopics on a piece of paper
New technologies and ways of buying and selling are transforming the lives of consumers.
To what extent do you agree or disagree with this opinion?
Where – We buy things in shops, in supermarkets, in markets and online.
How – By using our phone or by travelling to the supermarket.
Step 2
Ask yourself more questions if needed
- If you have asked yourself a few questions and you feel comfortable that you have most of an answer you can stop there. But if you feel like you need to generate some more ideas you can ask yourself a few more questions.
- Learn more ways to think of ideas in our IELTS Writing Task 2 Course
Do a course designed by a former IELTS Examiner with hundreds of 5* reviews. - Find out what really improves your score in the exam

